When it comes to your vehicle’s ignition system, understanding the components and how they work can be crucial for maintenance and performance optimization. Among these components, ignition coils play a significant role. This article will delve into the differences between Coil-on-Plug (COP) ignition systems and traditional ignition systems, providing a comprehensive understanding of each.
What is an Ignition Coil?
An ignition coil is an essential part of your vehicle’s ignition system, responsible for transforming the battery’s low voltage to the high voltage needed to create an electric spark in the spark plugs. This spark ignites the fuel mixture in the engine’s cylinders, enabling the engine to run.
Traditional Ignition Systems
Overview
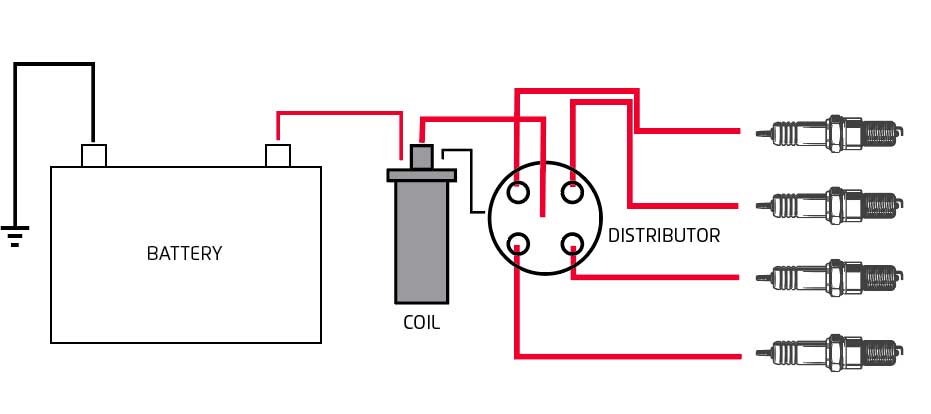
Traditional ignition systems have been around for decades and typically include a single ignition coil, distributor, rotor, and spark plug wires. This setup distributes the high-voltage spark from the ignition coil to each spark plug in a specific firing order.
Components
- Single Ignition Coil: Generates high voltage.
- Distributor: Routes the high voltage from the coil to the correct cylinder.
- Rotor: Spins inside the distributor to direct the spark to the correct plug.
- Spark Plug Wires: Carry the high voltage from the distributor to the spark plugs.
Advantages
- Simplicity: Easier to diagnose and repair.
- Cost: Generally cheaper due to fewer parts.
Disadvantages
- Wear and Tear: Mechanical parts like the distributor and rotor are prone to wear, leading to maintenance issues.
- Performance: Can be less efficient, particularly at higher engine speeds.
Coil-on-Plug (COP) Ignition Systems
Overview
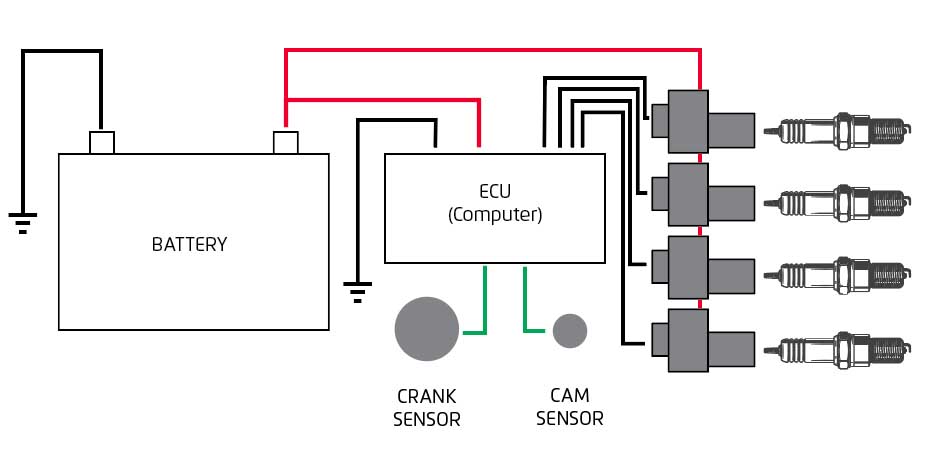
Coil-on-Plug systems represent a modern advancement in ignition technology. In a COP system, each cylinder has its own ignition coil mounted directly on top of the spark plug. This setup eliminates the need for a distributor and spark plug wires.
Components
- Individual Ignition Coils: Each cylinder has its own coil.
- Spark Plugs: Directly connected to their respective coils.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): Manages the timing and firing of each coil.
Advantages
- Improved Performance: More precise spark timing and stronger spark, leading to better combustion efficiency.
- Reliability: Fewer moving parts, reducing wear and potential points of failure.
- Efficiency: Often results in better fuel economy and reduced emissions.
Disadvantages
- Cost: Higher initial cost due to more components.
- Complexity: More difficult to diagnose and repair without specialized equipment.
Key Differences
- Configuration: Traditional systems use a single coil and distributor, while COP systems have individual coils for each cylinder.
- Maintenance: Traditional systems require periodic maintenance of the distributor and spark plug wires. COP systems have fewer maintenance needs but can be more complex to repair.
- Performance: COP systems provide better performance through more efficient spark delivery and timing.
- Cost: Traditional systems are typically less expensive to install and maintain, while COP systems can offer long-term savings through improved efficiency and reduced maintenance.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Coil-on-Plug and traditional ignition systems is essential for anyone interested in vehicle maintenance and performance. While traditional ignition systems offer simplicity and lower initial costs, COP systems provide superior performance, reliability, and efficiency. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, knowing these differences can help you make informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and upgrades.
For more information on ignition systems and other automotive technologies, visit MotoRad.com’s tech section. Stay tuned for more expert insights and tips to keep your vehicle running at its best.
